|
GeneHarbor's pipeline includes novel enzymes and processes for the
production of pharmaceutical products, neutraceutical
products and high-value added food ingredients.
The Company also operates its own
manufacture facility that industrially manufactures biochemicals
of the highest standard. The products and product pipeline include:
reduced glutathione; the derivative of glutathione, SAMe,
NAD +, NMN.
Main Products
  
L-Glutathione
reduced(GSH) S-Acetyl glutathione (SAG) NAD
  
NADH Recombinant
Protein A Recombinant Protein G
Products
Description
GSH:
Name: L-glutathione reduced, GSH
Formula: C10H17N3O6S
MW: 307.32
CAS#: 70-18-8
Purity : ≥ 98.5% (HPLC)
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Storage: 2-8℃
Glutathione-The
World’s Most Powerful Antioxidant in Your Body!
Every cell in your body requires an adequate supply to function
and to stay healthy. It’s your body’s super defender against illness,
infection, toxins, and disease. GSH is critical to optimum brain
function, and is also your body’s first line of defense against diseases
of aging and the harmful effects of stress and overexertion.
Glutathione is
Essential to Health Glutathione’s three
major roles in the body are summarized by the letters A-B-C(Antioxidant, Blood Booster and Cell
Detoxifier),these are the three critical processes driven by glutathione.
Why Should We Need GSH
Supplement?
Research has shown that individuals who have low levels of
glutathione are susceptible to chronic illness. Research shows that GSH
levels decline by 8% to 12% per decade, beginning at the age of 20.
Levels of glutathione are further reduced by continual stress upon
the immune system such as illness, infection, and environmental
toxins. As we now know, a lowered immune system can bring about illness
and disease. This is a ferocious cycle. While you need glutathione for a
productive immune system, a weakened immune system hampers the production
of glutathione.
The Power of
Glutathione
Glutathione has been shown to slow down the aging
process, detoxify and improve liver function, strengthen the immune
system, and reduce the chances of developing
cancer. Glutathione also works to help improve mental
functions, increase energy, improve concentration, permit increased
exercise, and improve heart and lung function.
Applications
Glutathione
is widely used in pharmaceuticals, health functional foods, dietary
supplements, cosmetics etc.
NAD (Oxidized Coenzyme I):
Names: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide;
CoenzymeⅠ; CoⅠ; NAD; NAD+.
Formula: C21H27N7O14P2
MW: 663.43
CAS#: 53-84-9
Purity: ≥95% (ADH); ≥98% (HPLC)
Appearance:
White powder
Storage:2-8℃
Description
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide,
abbreviated NAD+, is a coenzyme found
in all living cells. The compound is a dinucleotide,
since it consists of two nucleotides joined
through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base
and the other nicotinamide
.
Functions
Nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide has several essential roles in metabolism.
It acts as a coenzyme in redox reactions,
as a donor of ADP-ribose moieties in ADP-ribosylation reactions,
as a precursor of the second
messenger molecule cyclic
ADP-ribose, as well as acting as a substrate for bacterial DNA
ligases and a group of enzymes called sirtuins that
use NAD+ to remove acetyl
groups from proteins. In addition to these metabolic
functions, NAD+ emerges as an adenine nucleotide that can be
released from cells spontaneously and by regulated mechanisms, and
can therefore have important extracellular
roles.
The
enzymes that make and use NAD+ and NADH are important in both
current pharmacology and
the research into future treatments for disease. Drug
design and drug development exploits NAD+ in three ways:
as a direct target of drugs, by designing enzyme
inhibitors or activators based on its structure that change
the activity of NAD-dependent enzymes, and by trying to inhibit
NAD+ biosynthesis.
The
coenzyme NAD+ is not itself currently used as a treatment for any
disease. However, it is potentially useful in the therapy of neurodegenerative
diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson
disease. NAD+ is also a direct target of the drug isoniazid,
which is used in the treatment of tuberculosis,
an infection caused by Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Isoniazid is a prodrug and
once it has entered the bacteria, it is activated by a peroxidase,
which oxidizes the compound into a free
radical form. This radical then reacts with NADH, to
produce adducts that are very potent inhibitors of the enzymes enoyl-acyl
carrier protein reductase, and dihydrofolate
reductase. In December 2013 a remarkable result concerning
the ability of NAD to reverse mitochondrial aging was reported by a team
led by David Sinclair. In an experiment with mice, Sinclair found that
2-year-old mice given NAD for just one week had significantly improved
nuclear-mitochrondrial communication.
Applications
NAD
is widely used in drugs, research, diagnostic, dietary supplement ,
synthesis etc.
NADH:
Name:
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide , reduced form (disodium salt)
Formula:
C21H27N7O14P2Na2
MW:
709.4
CAS#: 606-68-6
Purity:
≥95% (ADH); ≥98% (HPLC)
Appearance:
White powder
Storage:2-8℃
What
is NADH ?
NADH,
biologically known as Coenzyme 1, is the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) with the
addition of high energy hydrogen (H), which
provides energy to the cell. NADH is necessary for thousands of
biochemical reactions within the
body and is found naturally in every living cell. NADH plays a key role in the energy production of
cells, particularly in the brain and central nervous system. The more NADH a cell has
available, the more energy it can produce to
perform its process efficiently. NADH stimulates cellular
production of the eurotransmitters
Dopamine, Noradrenaline, and Serotonin, thereby improving mental clarity, alertness and
concentration.NADH is directly involved in the body’s cellular immune defense system and the more
NADH in your body, the better the DNA repair
system functions.
NADH
in Food and Dietary Sources
NADH
is present in every living cell, animal or plant.
It
should be noted that most NADH we take in from foods is destroyed during
the cooking process. Even
if our diets consisted mostly of raw meat or fish, the greater part of
the NADH present in these foods would be degraded by the stomach gastric
acid system in our bodies.
Dietary
supplement
NADH
(nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is an amazing dietary supplement that
has an abundance of beneficial effects on a cellular level. Many
individuals take NADH as an energy supplement because it can effectively
increase ATP production. ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the primary
energy carrier of the body. NADH plays a key role in cellular energy
production, particularly in the brain and central nervous system.
NADH
is widely used to help supplement many cases involving Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
(CFS), Fibromyalgia, Parkinsons, Alzheimers, Depression, Jet Lag, ADHD
(Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder), and more. What was commonly
used to help relieve symptoms of conditions resulting in lack of energy,
is now used by executives, athletes, and everyday people to increase
energy, improve mental clarity, and improve physical performance. NADH
also is a vital part in making the popular supplement CoQ10 effective
into an antioxidant. NADH is taken regularly by hundreds of thousands of
people worldwide who experience positive results from its natural
benefits.
NMN:
Name:
Formula:
MW:
CAS#:
Purity:
Appearance:
r
Storage:℃
Description
Applications
Protein
A:
Name:
Recombinant Protein A
MW: 22kD (SDS-PAGE; see Fig.1)
pH
range: 2.0-11.0
Purity:
≥98% (SDS-PAGE,HPLC)
Activity:
≥95% (human IgG binding activity)
Appearance:
White powder
Storage:
2-8℃
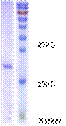
Figure
1: Protein A
(SDS-PAGE)
Description
Recombinant
Protein A is a type I membrane protein covalently linked to the cell wall
of most strains of the Gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
It has high affinity to IgG from various species, for instance human,
rabbit and guinea pig, but only weak interaction with bovine and mouse.
Protein A interacts with antibodies through two distinct binding events:
the “classical” binding site on the Fc portion of human IgG1, IgG2, and
IgG4, and the “alternate” binding site found on the Fab portion of human
IgG, IgM, IgA, and IgE that contain heavy chains of the VH3 subfamily.
Applications
The
properties of protein A enables it as a powerful affinity ligand for
several immunological and
purification applications. High selectivity and good physiochemical stability
have made protein A the preferred generic ligand for affinity
purification of antibodies and molecules tagged with an antibody
Fc-region. Protein A can also be used in various immunochemical assays
including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA applications
by conjugation with different reporter molecules, such as fluorescent
dyes (FITC), enzyme markers (peroxidase, β-galactosidase, alkaline
phosphatase), biotin, and colloidal
gold. Immunoprecipitation studies with protein A conjugated to
beads are also commonly used to purify proteins or protein complexes
indirectly through antibodies against the protein or protein complex of
interest.
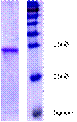
Figure 2:Protein G
(SDS-PAGE)
Protein
G
Name
: Recombinant Protein G
FW
: 25kd (SDS-PAGE, see Fig.2)
pH
range : 2.0-11.0
Purity
: ≥98% (HPLC)
Appearance
: White powder
Storage
: 2-8℃
Description
Protein
G is a bacterial cell wall protein expressed at the cell surface of
certain group C and group G Streptococcal strains.
It
has affinity for both Fab- and Fc-fragments of human IgG by independent
and separate binding sites. Binding to the Fc region of immunoglobulins
from several species by a non-immune mechanism exhibits great affinity
for almost all mammalian immunoglobulin G (IgG) classes, including all
human IgG subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4) and also rabbit, mouse,
and goat IgG. Protein G bound all tested monoclonal IgG from mouse IgG1,
IgG2a, and IgG3, and rat IgG2a, IgG2b, and IgG2c. In addition,
polyclonal IgG from man, cow, rabbit, goat, rat, and mouse bound to
protein G, whereas chicken IgG did not. Protein G has also been shown
to bind human serum albumin but at a site that is structurally separated
from the IgG-binding region. Protein G shows a broader range of binding
to IgG subclasses than staphylococcal protein A. This applies to
polyclonal IgG from cow, rat, goat, human and rabbit sources as well as
several of rat and mouse monoclonal antibodies.
Applications
Protein
G was found to be a powerful reagent for the detection of IgG,
and consequently the antigen against which these antibodies are
directed. It was used in Western blot analyses to detect various
antigen-antibody complexes on nitrocellulose membranes. Moreover, protein
G is widely used as a ligand coupled to resins in affinity chromatography
for antibody purification.
|